Name: Sociotechnical System (STS)
Based on: Social System
Abstract System: This system has been identified as an abstract system that cannot be implemented directly. The abstract system establishes a shared pattern of characteristics that any system can use to describe its unique characteristics when referenced in the 'based on' list above. These references are described using a generalization association in UML.
The purpose of a sociotechnical system is to enhance an organisms ability and performance using of elements from natural systems or designed physical systems (engineered systems). This allows productivity improvements to be achieved through the fully integrated use of natural systems elements or technology.
Organisms such as bees, ants and beavers create structures that are formed from natural system elements. These form structures that provide shelter or storage of food.
Designed Physical Systems (Technology) are typically used in relation to a Human Activity System (HAS). These are generally used as part of a organizational capability that includes people, process and technology elements. See the Organizational Capability System Description for more information on these socialtechnical systems.
This section adds to the information in the system description for the social system.
Systemic Measurable Variables
Productivity: Demonstrated increase in work effectiveness
Accuracy: Reduced number of errors
Systemic Capabilities or Functions
The capabilities or functions the system provides. These capabilities are generally the same or enhanced through the use of technology.
This section adds to the information in the system description for the social system.
Identify the key stakeholders and their concerns for this system. Each stakeholder is identified and their concerns and interests are identified. The list below is an example. Each system will have a specific set of stakeholders and concerns.
- Owner / manager: Does the improvement in productivity justify the investment in technology?
- System Architect: Can the users of the system interact and achieve the benefits of the technology?
- People in the environment Will the results of using the system capabilities be better?
- Change Agents Are we capable of integrating and using the technology to deliver the benefits?
- People who are part of the system Will I be able to use the technology to achieve my contribution to the enterprise?
This section adds to the information in the system description for the social system.
There may be specific environmental elements for any:
- Ecosystem Services that are included
- Designed Physical Systems (Technology) that are included.
This section adds to the information in the system description for the social system.
System Element: Identification
The additional elements added to the social system are:
- Ecosystem Services
- Designed Physical Systems (Technology).
The social system is extended with technology to the folowing:
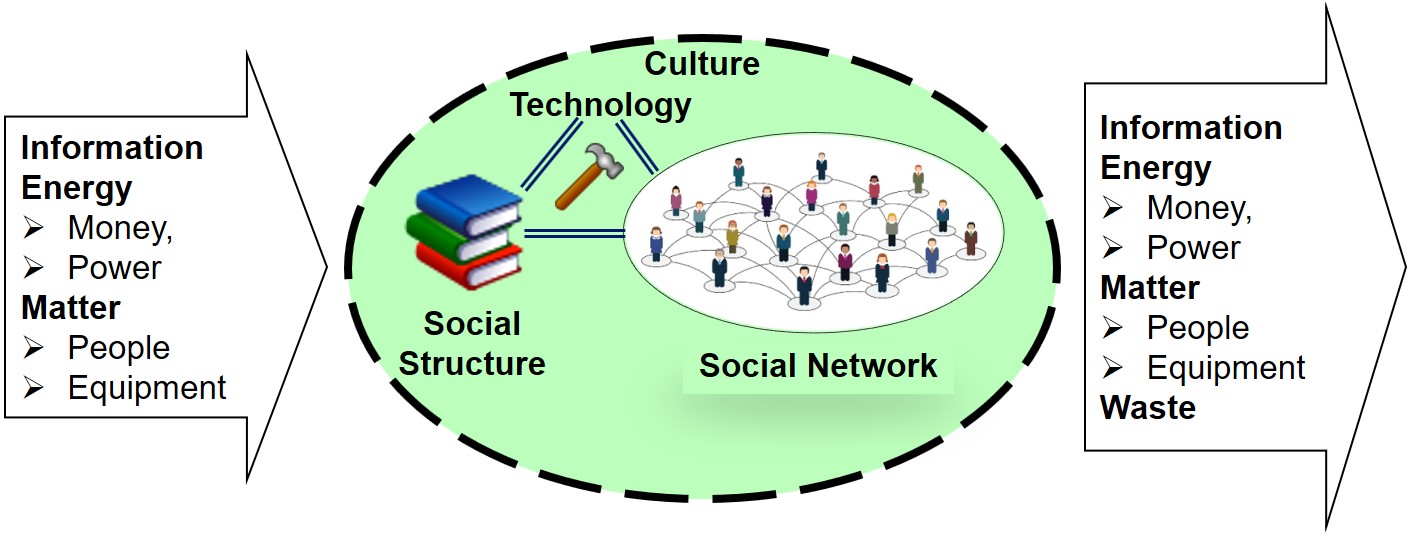
System Element: Relationships
For Ecosystem Services
An organism with the appropriate abilities can take benefits from ecosystem services. These are natural system abilities that ensure that the organisms thrive in their habitats.
For technology in human activity systems, the following additional relationships are formed. This use of technology includes human factors analysis etc.
Technology includes any type of technology. Information Technology is one type of technology. These elements form the basis for an organisational capability as a system. These capabilities are then realised in a team using the team model.
The system element relationships are also described in the relationship section of the Capability System.
People <--> Activity / Decision Descriptions as part of a Process Description
A person is assigned to a role to carry out a one or more activity / decision descriptions.
This is a work assignment and is utilizing the skills, knowledge and experience of the person assigned to the role.
In addition to doing the work, people also are responsible for improving the work. (dual nature of work).
Technology <--> Activity / Decision Descriptions as part of a Process Description
People use technology to help carry out their work. The Activity Description identifies the steps in the activity where technology is used to support the completion of the activity. These are generally called 'Technology Interaction Points.
An information technology system (captures data, and performs calculations and creates displays of information (reports and visual displays). This information is also maintained and shared across the organisation.
The people who look at this interface are typically business analysts and create Use Cases / Stories for developers to create applications and data bases. These are generally on the infrastructure provided for the information technology systems.
People <--> Technology
People interact with technology to help perform the activity. This interaction focuses on the human factors interface to the technology. This interaction ensures that people are able to obtain the benefits from the use of technology.
People interact with the information technology systems in either an intuitive way or are frustrated by the way the system works. This Human computer interface area determines both productivity and acceptance. Both of these areas are important to realize the benefits of the use of technology.
This section adds to the information in the system description for the social system.
Configuration / Scenario:
Describes any configuration / scenario attributes for a specific system-of-interest. This may not be appropriate for all system descriptions (e.g. patterns or abstract systems).
Cyclical (Repeating / Regular) Processes
For organisms including ecosystem services into their sociotechnical system.
- Most of the cyclical processes are using the natural abilities of the organism to manage the ecosystem services.
When a sociotechnical system that includes technology (designed physical systems) to be used by people, the cyclical processes:
- require some training
- require appropriate time allocation for use of the technology (breaks and protective equipment, etc)
- requires support and maintenance
Development Life Cycle Processes
Organisms can improve their use of ecosystem services through repeated use and learning.
Designed Physical Systems (Technology) typically involves separate development through an 'enabling' system to develop or produce the technology. This information is typically included in the human activity system Enterprise which generally provides the full life cycle support for this technology.
The following references support this type of system-of-interest.
Book References
Re-Creating the Corporation, Russell Ackoff
Systems Thinking, Systems Practice, Peter Checkland
Organization Design, Jay Galbraith
Information, Systems, and Information Systems, Peter Checkland and Sue Holwell
This is a fundamental part of the STAR model from Jay Galbraith (now used in the meta model of an organisation).
- See On Purposeful Systems
- See Organization Design
- See Also: Socio Technical Centre (STC) at the University of Leeds, UK
- See Also: BCS Sociotechnical Group