Abstract System
The following definitions of system and architecture are being used:
- ISO 9000:2015: System: set of interrelated or interacting elements
- ISO 15288:2015: System: combination of interacting elements organized to achieve one or more stated purposes
- ISO 15288:2023: System: arrangement of parts or elements that together exhibit a stated behaviour or meaning that the individual constituents do not.
- ISO 15288:2023: System Element: discrete part of a system that can be implemented to fulfil specified requirements
- INCOSE 2019: A system is an arrangement of parts or elements that together exhibit behavior or meaning that the individual constituents do not.
- ISO 42010:2011: Architecture: [of a system] fundamental concepts or properties of a system in its environment embodied in its elements, relationships, and in the principles of its design and evolution
- ISO 42010:2022: Architecture: [of an entity] fundamental concepts or properties of an entity in its environment and governing principles for the realization and evolution of this entity and its related life cycle processes.
- ISO 15288:2023: Architecture: [of a system] fundamental concepts or properties of an system in its environment and governing principles for the realization and evolution of this system and its related life cycle processes.
The following definitions from system thinking authors are being used:
Russell Ackoff Definition: System: A system is a whole consisting of two or more parts that satisfies the following five conditions:
- The whole has one or more defining properties or functions
- Each part of the set can affect the behavior or properties of the whole
- There is a subset of parts that is sufficient in one or more environments for carrying out the defining function of the whole; each of these parts is necessary but insufficient for carrying out this defining function.
- The way that each essential part of a system affects its behavior or properties depends on (the behavior or properties of) at least one other essential part of the system.
- The effect of any subset of essential parts on the system as a whole depends on the behavior of at least one other such subset.
It follows from the definition of a system that its properties derive from the interactions of its parts, not their actions taken separately. A system is a whole whose essential properties, its defining functions, are not shared by any of its parts. A system is a whole that cannot be divided into independent parts without loss of its essential properties or functions.
Donella Meadows: System: A set of elements or parts that is coherently organized and interconnected in a pattern or structure that produces a characteristic set of behaviors, often classified as its "function" or "purpose".
-
A system is more than the sum of its parts
-
Many of the interconnections in systems operate through the flow of information.
-
The least obvious part of the system, its function or purpose, is often the most crucial determinant of the system's behaviour.
-
System structure is the source of system behavior. System behavior reveals itself as a series of events over time.
Ludwig von Bertalanffy System: a set of elements standing in inter-relations among themselves and with environment. The characteristics of the complex, therefore, compared to those of the elements, appear as "new" or "emergent." "What we can say, while we can conceive of a sum as being composed gradually, a system as total of parts with its interrelations has to be conceived of as being composed instantly."
"It is generally agreed that 'system' is a model of general nature, that is, a conceptual analog of certain rather universal traits of observed entities. "
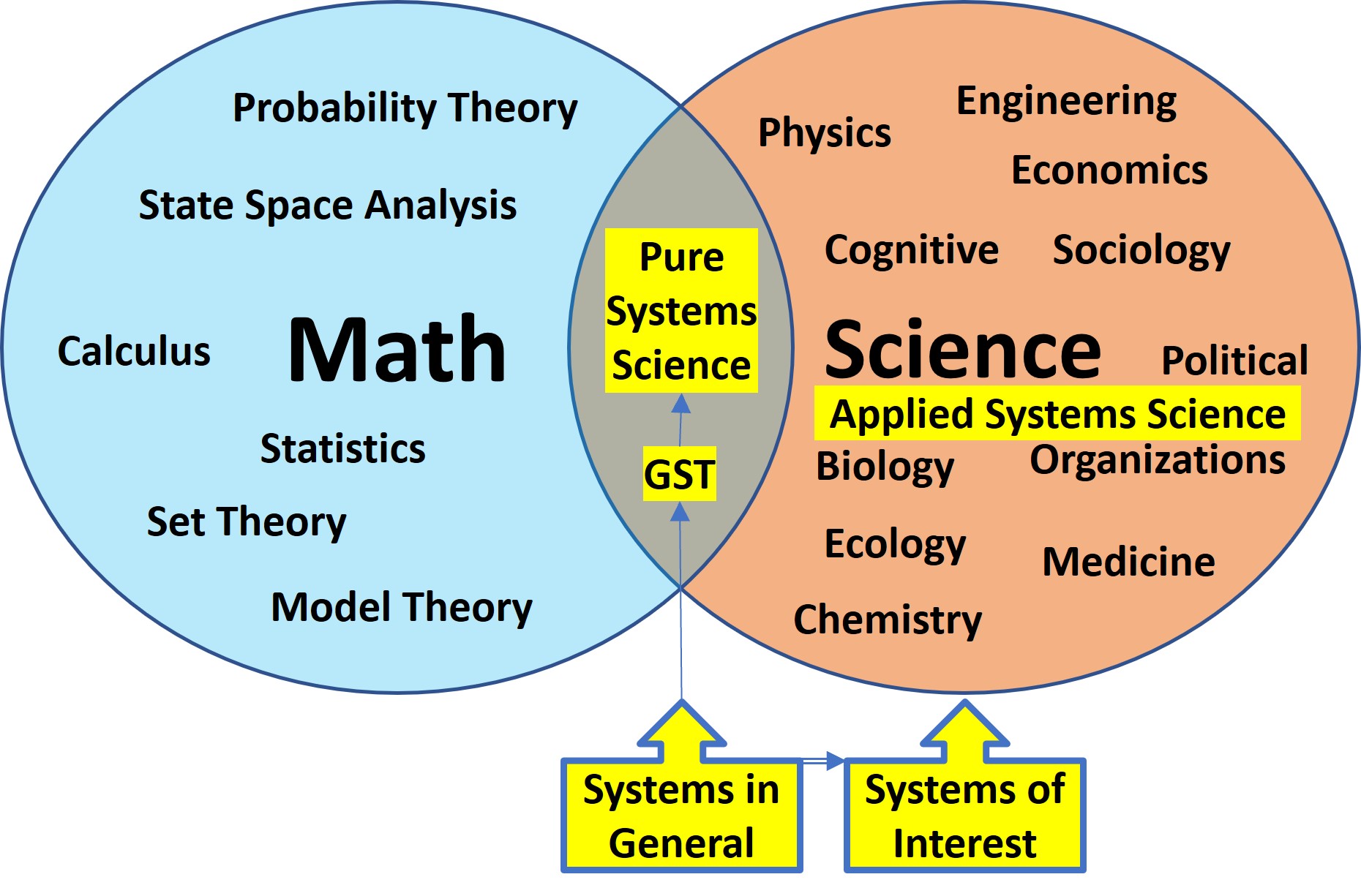
This general system concept is based upon mathematics and provides a general system approach for developing information about a system-of-interest. The following picture highlights this position.
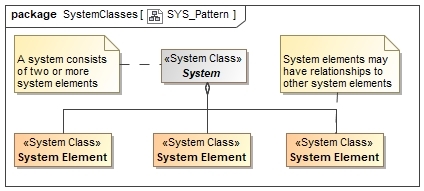
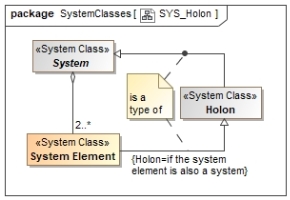
A simple pattern for a model of an abstract system is the following:
A Holon is a system element that is also a system.
The following diagram identifies some of the key elements that are common across the various definitions:
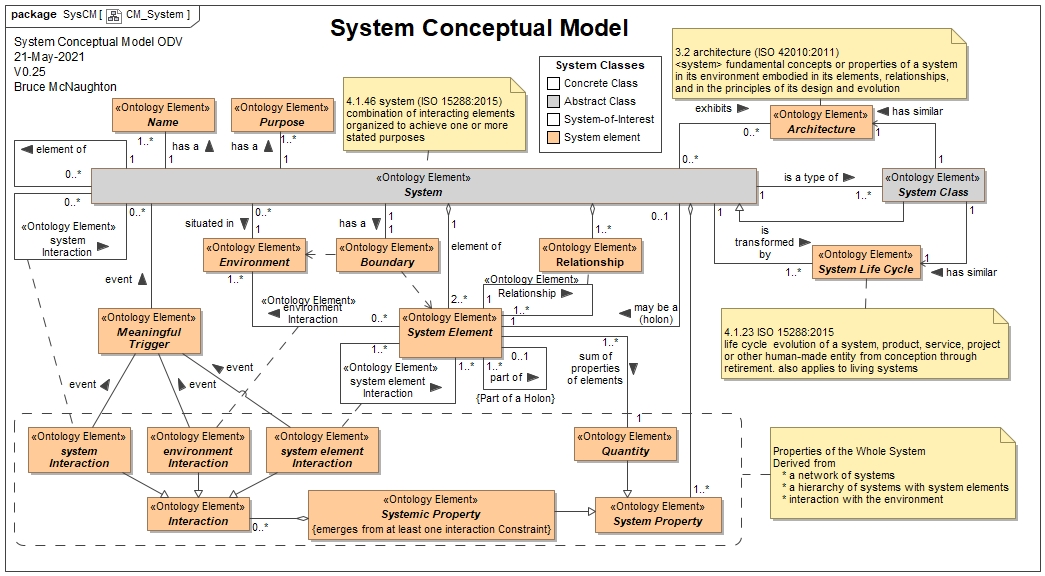
Systemic properties emerge from the interaction of the system elements with other system elements or other systems and with the environment.
The system concepts related to a system includes:
These concepts form a part of a system body of knowledge that provide a language (symbol system), methods, techniques, and models to be used to understand things as a system.
The methods and tools include:
-
Soft Systems Methodology (SSM)
-
System Engineering
-
System Dynamics
-
Complex Adaptive Systems